👨🏫 Outline
Why do we need a financial system?
Finance is about getting funds from people who have more funds than they need to people who can use them more profitably. For example:
- You are saving money for retirement. You have money that you aren’t spending.
- A local entrepreneur needs money to start a profitable local business.
- The financial system gets money from you to the entrepreneur.
- Because the entrepreneur can put your funds to work profitably, they can return some of the profit to you. This profit induces you to invest.
| Have Funds to Save: | Financial System: | Need Funds Now: |
|---|---|---|
 | ➡️ (Funds) |  |
Physical Capital refers to Machines, Factories, Office Buildings, Infrastructure, etc.
Working Capital refers to the funds a company must have on hand to meet day to day expenses (such as payroll, raw materials, etc.).
Companies need Physical and Working Capital to be competitive. To pay for these, they raise funds from savers via the financial system, as described, above. These funds are known as Financial Capital .
In summary: Savings ⇨ Financial Capital ⇨ Physical + Working Capital.
Where do Firms Get Their Funds?
- A Bond is a promise by a large company or other very large borrower to pay you specific amounts of money at specific times in the future.
- For example, if Tesla wants to raise $100M, and is willing to pay an 8% interest rate, it can divide the $100M into chunks of $1,000. It sells bonds with a “face value” of $1,000. In one year, it will pay the owner of that bond $1,000 + 8% interest ($80.) It can use an investment bank like Morgan Stanley to sell 100,000 of these bonds to investors for a total of $100M.
- A Stock is an ownership share in a corporation.
- For example, if you start a company, you could divide the company into 100,000 ownership shares. Whenever the company distributes its profits, it distributes them pro-rata based on ownership share. Anyone who owns one share owns 1/100,000th of the company and gets 1/100,000th of the profits being distributed. Likewise, anyone who owns 1,000 shares owns 1% of the company and gets 1% of the distributed profits (called dividends).
- A Security is a standardized and tradeable financial claim on future cash flows, such as a stock or a bond.
- Retained earnings are profits the corporation made. They invest it back into the company (retained profits). These are internal funds because they are generated by the firm.
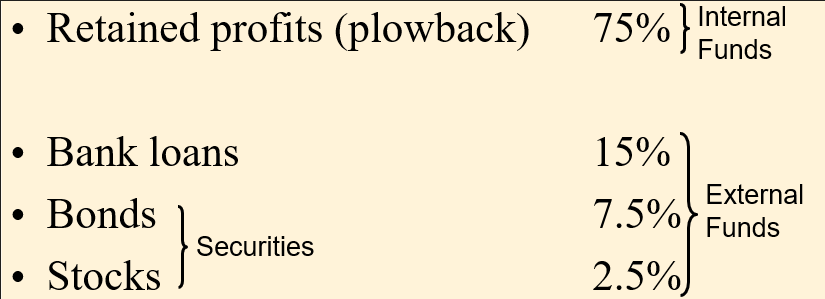
🙋 Why is the percentage for stocks so low when the stock market is so valuable?
✔ The above table was compiled by the professor based on Federal Reserve Flow of Funds data. Because it refers to the flow of funds in the US economy, it must be interpreted carefully. Bank loans and bonds are frequently paid off and then “rolled over.” When an old debt is “rolled over,” it is essentially the same debt, but it will show up an additional time in this data. In contrast, stocks are only issued once, so they only show up once. Further, they are most frequently issued when the company is young, for a small amount of money. Their price often increases dramatically over time, but only the original, low price, issuance will show up in the flow of funds data. ✅
Other Functions of the Financial system
The following list breaks down the following slide:

- Provide ways to transfer economic resources through time, across borders and among economic sectors and industries.
- We saw in the previous section that when you invest for retirement, you transfer your purchasing power “through time,” deferring consumption today for larger consumption in the future.
- You can also invest “across borders” by purchasing financial instruments in other countries.
- Provide essential information to facilitate and coordinate decentralized decision-making
- Stock price tracks the true health of a company, assessing its stability, financial soundness, market share strength, financial performance, etc. Stock price aggregates and consolidates information about that firm. Financial markets are forward looking, taking into account the future prospects of the firm.
- Provide ways to manage risk
- Example 1: If I own an unincorporated company as a sole proprietor, creditors can come after me for all of the company’s debts. But if I own a share of stock in a corporation, creditors can’t come after me personally.
- Example 2: Diversification can reduce risk by “not keeping all eggs in one basket.”
- Provide a means to clear and settle payments to facilitate trade
- Provide a means for pooling of savings and subdividing ownership shares
- Remember that the ultimate source of financial capital is people’s savings. The amount of financial capital required to start a modern company is far greater than the amount of savings owned by all but the richest families. Dividing companies into shares of stock facilitated the pooling of savings and made possible the rapid economic expansion of the past 150 years.
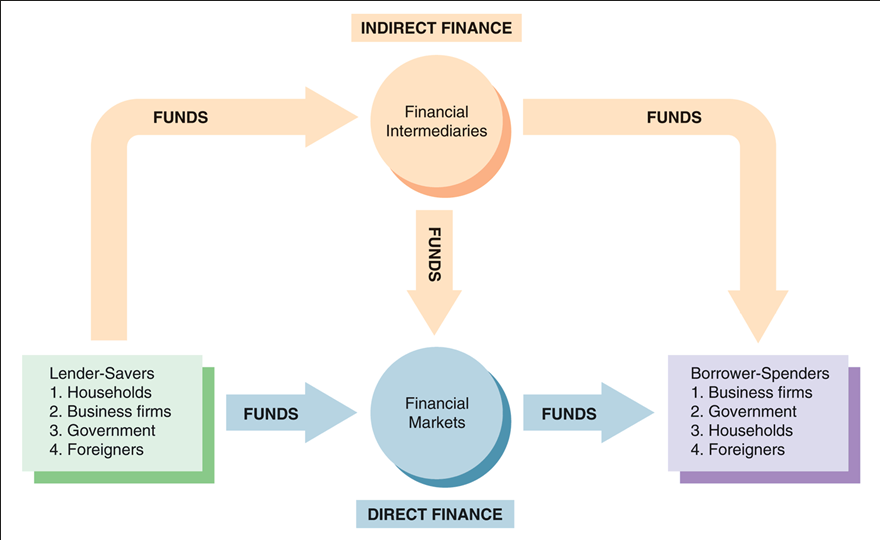
With Direct finance , the Lender/Saver determines which Borrower/Spender they invest in. With Indirect Finance , a bank or other financial intermediary makes that choice.
As we can see from the following chart:
- The US is more market oriented (Direct Finance)
- Germany and Japan are more bank oriented (Indirect Finance)
- Canada is intermediate
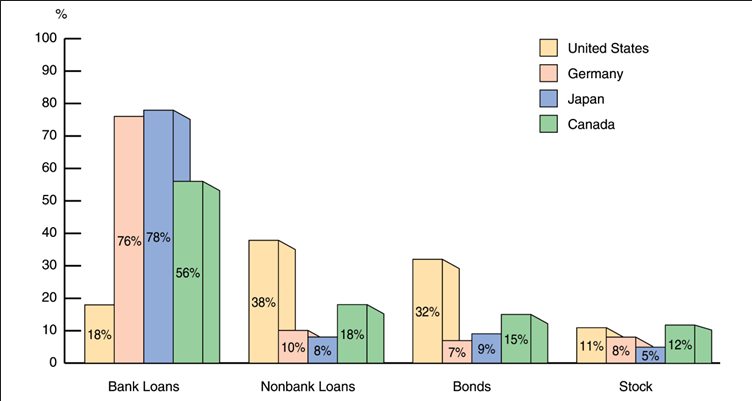
In general, East Asia and Europe are more bank centered, whereas, US, UK, and Australia are more market centered. One theory why the US has more direct finance is that it’s common law legal system provides better protection for direct investments. Because Stock and Bond investors are better protected, they are more confident and provide more of the financing. There is less of a need for financial intermediaries like banks.
Feedback? Email rob.mgmte2000@gmail.com 📧. Be sure to mention the page you are responding to.